Difference between revisions of "Inspection with an electron microscope II"
m |
m |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
|} | |} | ||
The relative X-ray analysis of a normal area gave one peak: Al. The white dots are Fe | The relative X-ray analysis of a normal area gave one peak: Al. The white dots are Fe | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Conclusion at 2am == | ||
| + | It might be that the dark gray areas seen on the kapton and Lamina-thin straws after radiation are due to the same process. They appear to be casued | ||
| + | by higher concentration of O indirectly induced by radiation. This process takes time and it looks that after 3 years of normal (low radiation) | ||
| + | operation of a stone kapton straw a difference (darker gray areas) can be observed with the EM but not with the X-ray analysis. As after an equivalent | ||
| + | of 44 years of radiation the straw (Lamina-thin) shows a big increase in dark areas or "black pits" the straw is still operational. | ||
| + | The Lamina-thick straw does not show any effect at all. | ||
Revision as of 03:10, 12 March 2010
Contents
Stone kapton straw
Pristine
The relative X-ray analysis of a normal area gave three peaks C, Al, and O. The magnitude of the peaks compared as C > Al > O. White spots are Ca = C = O > Al > P
Under source (irradiated)
The relative X-ray analysis of a normal area gave three peaks C, Al, and O. The magnitude of the peaks compared as C > Al > O . The X-ray analysis of a dark spot gave C = 0 > Al. Also the darker the spot the more O present.
3 years under voltage (big prototype)
The relative X-ray analysis of a normal area gave three peaks C, Al, and O. The magnitude of the peaks compared as C > Al > O, also the darker areas gave the same relative C > Al > O.
Lamina thin straw
The relative X-ray analysis of a normal area (light gray) gave three peaks C, Al, and O. The magnitude of the peaks compared as Al > C > O. The dark spots showed O > Al > C or O = Al > C . White spots are Ca = C = O > Al > P
Lamina thick straw
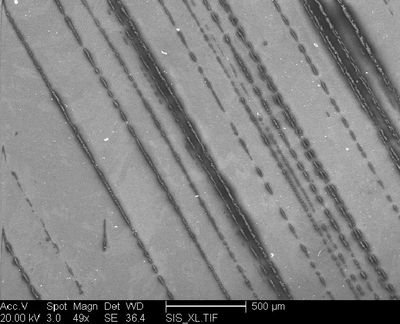
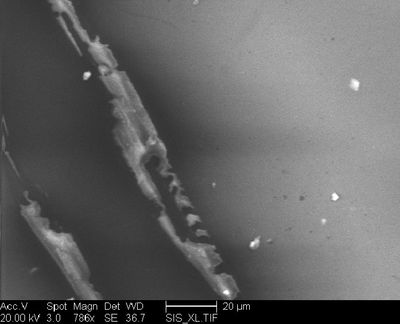
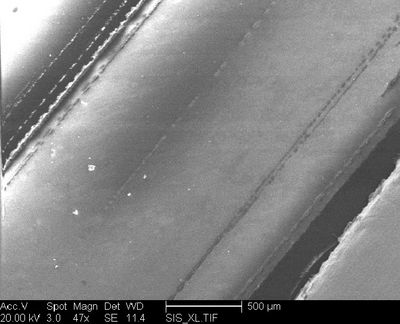
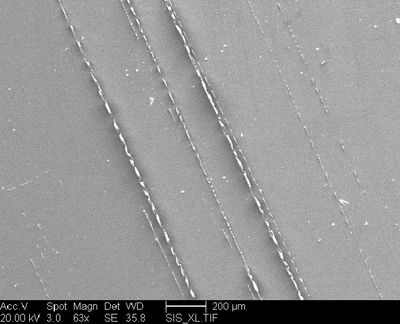
The relative X-ray analysis of a normal area gave one peak: Al. The white dots are Fe
Conclusion at 2am
It might be that the dark gray areas seen on the kapton and Lamina-thin straws after radiation are due to the same process. They appear to be casued by higher concentration of O indirectly induced by radiation. This process takes time and it looks that after 3 years of normal (low radiation) operation of a stone kapton straw a difference (darker gray areas) can be observed with the EM but not with the X-ray analysis. As after an equivalent of 44 years of radiation the straw (Lamina-thin) shows a big increase in dark areas or "black pits" the straw is still operational. The Lamina-thick straw does not show any effect at all.